
Lang Andrew
Social Origins and Primal Law
DR. WESTERMARCK'S THEORY
As to exogamy, Dr. Westermarck explains it by 'an instinct' against marriage of near kin. Our ancestors who married near kin would die out, he thinks, and they who avoided such unions would survive, 'and thus an instinct would be developed,'59 by 'Natural Selection.' But why did any of our ancestors avoid such marriages at all? From 'an aversion to those with whom they lived.' And why had they this aversion? Because they had an instinct against such unions. Then why had they an instinct? We are engaged in a vicious circle. 'Lastly it is not scientific to use the term instinct of this kind of thing.'60
MR. MORGAN'S THEORY
As to Mr. Morgan's theory, in his Ancient Society (1877), of a movement of sanitary and moral reform, which led to prohibition of 'consanguine marriages' I shall return to it in a later part of this essay ('Other Bars to Marriage'). Here it will be found that Mr. Morgan is the source of certain other theories which we are to discuss, a fact involving a certain amount of repetition of arguments already advanced.
RETURN TO THE AUTHOR'S THEORY
We conclude, provisionally, that exogamy, for various reasons of sexual jealousy, and perhaps of sexual superstition, and of sexual indifference to persons familiar from infancy, may, at least, have tended to arise while each little human group was anonymous; before the acceptance of totem names by local groups. But this exogamous tendency, if it existed, must have been immensely reinforced and sweepingly defined when the hitherto anonymous groups, coming to be known by totem names, evolved the totem superstitions and tabus. Under these, I suggest, exogamy became fully developed. Marriage was forbidden, amours were forbidden (there are exceptional cases), within the totem name. This law barred, of course, marital relations between son and mother, between brother and sister, but, just as it stood, permitted incest between father and daughter, so long as the totem name was inherited from the mother. But that form of incest, in turn, came to be barred by another set of savage rules, which, whatever their origin, prohibit marriage within the generation. That set of rules, noted specially in Australia and North America, is part of what is usually styled 'The Class System.'
CHAPTER II
THE CLASS SYSTEM
Under this name appear to be blended, (1) the prohibition to marry within a division, which, in its simplest form, is said to cut the tribe into two 'classes' or 'phratries,' or 'groups;'61 (2) the prohibition to marry within the totem name; (3) the prohibition to marry within the generation, and within certain recognised degrees ('classes,' 'sections') of real or inferred kinship – 'too near flesh,' too close consanguinity, which, in their present condition, many Australian tribes undoubtedly regard as a bar to matrimony. But it does not follow that they originally held this opinion.
We shall first examine what authorities who differ from me, call the great 'bisection' of the tribe, into, say, Matthurie and Kirarawa, members of which must intermarry, the totem prohibition also remaining in force. It will here be suggested, in accordance with what has already been said, but contrary to general opinion, that the totemic prohibition is earlier than the prohibition of marriage between persons of the same segment of the 'bisection.' The opinions of most students appear, at present, to be divided thus. We hear that:
1. The exogamous division into two moieties, or 'phratries,' is earlier than the division of each into numerous totem kins. The totem kins are regarded as later 'subdivisions' of, or additions to, the two 'original' moieties.
2. Totem groups are earlier than the 'bisection' (though somehow, according to the same authors, the two moieties of the bisection bore totem names), but, before the 'bisection,' these totem groups were not exogamous. They only became exogamous when six of them, say, were arranged in one of the two moieties (phratries), now forbidden to marry, and another six in the other.
I venture to prefer, as already indicated, the system (3) that totem groups not only existed, but were already exogamous, before the great 'bisection' producing the 'phratries' came into existence, though I argue that 'bisection' is a misleading term, and that the apparent division was really the result of an amalgamation of two separate and independent local totem groups.
This theory (presently to be more fully set forth) is original on my part, at least as far as my supraliminal consciousness is concerned. I mean that I conceived myself to have hit on the idea in July 1902. But something very like my notion (I later discovered) had been printed by Dr. Durkheim, and something not unlike it was propounded by Herr Cunow (1894). Mr. Daniel McLennan had also suggested it: and I find that the Rev. John Mathew had stated a form of it in his Eagle-Hawk and Crow (1899), (pp. 1922, 93-112). Mr. Mathew's hypothesis, however, involves a theory of contending and alien races in Australia. This theory does not seem well based, but, however that may be, I recognise that Mr. Mathew's hypothesis of the origin of exogamy (p. 98), and of the origin of the 'phratries' or 'primary classes,' in many respects anticipates my own. He opposes Mr. Howitt's conclusions, and I may be allowed to say that I would prefer Mr. Howitt, owing to his unrivalled knowledge, as an ally. On the other hand, the undesigned coincidence of Dr. Durkheim's, Mr. Daniel McLennan's, Mr. Mathew's, and Herr Cunow's ideas with my own, raises a presumption that mine may not be untenable.
THE CLASS SYSTEM IN AUSTRALIA
Though the existence of what are called exogamous 'phratries' (two to each tribe) was made known, as regards the North American tribes, by Mr. Lewis Morgan (to whose work we return) in the middle of the nineteenth century, almost our earliest hint of its existence in Australia came from the Rev. W. Ridley, a learned missionary, in 1853-55. In Mr. McLennan's Studies in Ancient History62 will be found an account of Mr. Ridley's facts, as they gradually swelled in volume, altered in character, and were added to, and critically constructed, by the Rev. Mr. Fison, and Mr. A. W. Howitt. These gentlemen were regarded by Mr. McLennan as the allies of Mr. Morgan, in a controversy then being waged with some acerbity. He, therefore, criticised the evidence from Australia rather keenly. It is probable that Mr. Morgan and Mr. McLennan both had some right on their parts – seeing each a different side of the shield – though a few points in the discussion are still undecided. But it seems certain that the continued researches of Messrs. Fison and Howitt, reinforced by the studies of Messrs. Spencer and Gillen in Central Australia, have invalidated some of Mr. McLennan's opinions as to matters of fact.
Much trouble and confusion will be saved if we remember that, as has been said, under the 'classificatory system,' three sets of rules applying to marriage exist. The totem rule exists, rules as to marriage in relation to generations and so-called degrees of kindred (real or 'tribal') exist ('classes'), and, thirdly, there are the rules relative to 'phratries,' the phratries, being, I think, in origin themselves totemic. We shall mainly consider here the so-called 'bisection' of a tribe into two exogamous and intermarrying 'phratries,' while remembering Herr Cunow's opinion that a 'class' is one thing, a 'phratry' quite another.63
THE VARIETIES OF MARRIAGE DIVISIONS IN AUSTRALIA
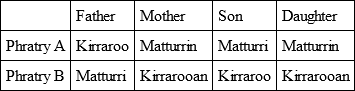
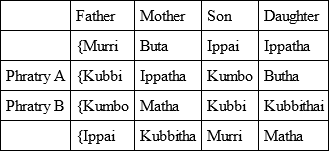
Perhaps the most recent, lucid, and well-informed writer on the various divisions which regulate the marriages of the Australian tribes is Mr. R. H. Mathews.64 In some regions, the system of two intermarrying phratries exists, without further subdivision (except in regard to totem kins). Sometimes each phratry is divided into two 'sections' (or 'classes'), making four for the tribe. Again, each phratry may have four 'subsections' or 'classes,' making eight for the tribe. Each phratry, like each 'class,' 'has an independent name by which its members are easily recognised.'
Obviously we need, of all tilings, to know the actual meanings of these names, but we do not usually know them. As we shall see, where a tribe has two 'phratries' and no subordinate 'classes,' the names of these 'phratries,' when they can be translated, are usually names of animals. In a few cases, as will later appear, when there are 'classes' under and in the 'phratries' their names seem to indicate distinctions of 'old' and 'young.' But Mr. Mathews nowhere, as far as I have studied him, gives the meanings of the 'class' names, some of which are of recent adoption. Mr. Mathews usually gives only 'Phratry A' and 'Phratry B.' We now cite his tables of the simple 'phratry' system, of the 'phratry' plus two classes system, and of the 'phratry' plus four classes system; making four, or eight, such divisions for the tribe.
'In describing the social structure of a native Australian community, the first matter calling for attention is the classification of the people into two primary divisions, called phratries, or groups – the men of each phratry intermarrying with the women of the opposite one, in accordance with prescribed laws.'
Mr. Mathews then mentions that some tribes have (1) this simple division only (of course, as a rule, plus totem kins). (2) Elsewhere each phratry is composed of two 'sections' (called by us 'classes'). (3) Elsewhere, again, each phratry has four sections (we need not discuss here the tribes where none of these things exist).
Mr. Mathews now gives tables representing the working of the system in each of the three cases.65
1
2
3
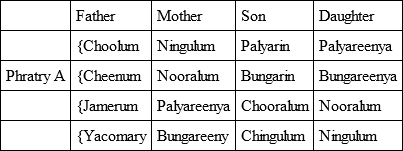
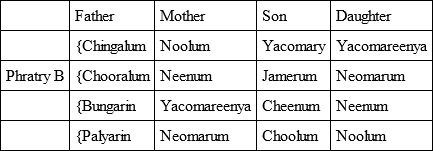
It will be seen that, under the simple phratry system, children of the female Matturrin are always Matturri and Matturrin, children of the female Kirrarooan are always Kirraroo and Kirrarooan. On the phratry plus two classes system, female Butha is mother of Ippatha and Ippatha of Butha for ever. On the phratry plus four classes system, female Ningulum has a Palyareena daughter, who has a Nooralum daughter, who has a Bungareenya daughter, whose daughter reverts to the original Ningulum class, and so on, ad infinitum. The women remain constant to their 'phratry,' and marry always the men of the opposite phratry.
It is to be observed that, by customary law, brothers and sisters actual (and not 'tribal') may never intermarry.66 In short, consanguinity is now fully understood by the natives, and too close unions are forbidden on the ground of consanguinity. It also seems that, though the blacks are all on the same level of material culture, yet reflection on marriage rules, and modification of these rules by additional restrictions and alterations, have been carried much further by some tribes than by others. I by no means deny, but rather affirm, that consanguinity is now understood, and that rules have in some tribes been consciously made, and altered, to avoid certain marriages as of 'too near flesh.' But I do not think that, at the beginning, the objection to consanguineous marriages, as such, can have been entertained, and I am not of opinion that, for the purpose of preventing such marriages, in the beginning, a horde was bisected into two phratries, and each phratry split up into totem groups. Rather, I conceive, certain primitive conditions of life led to the evolution of certain rules, independent of any theory about the noxiousness or immorality of marriages of near kin; and then reflection on those primal rules helped to beget moral ideas, and improvements on the rules themselves. In the original restrictions, morality, in our sense, was only implicitly or potentially present, though now it has risen into explicit consciousness. The tribes came to think certain marriages morally wrong, or physically noxious, because they were forbidden; such unions were not, in the first instance, forbidden because they were deemed physically injurious, or morally wrong. These ideas have, by this time, been evolved; but it does not follow that they were present at the beginning.
I took the liberty of laying a brief sketch of my own theory before Mr. Howitt, who, after considering it, was unable to accept it. He was kind enough to send me a summary account of many varieties of institutions, which, as we have seen, prevail – from tribes with totems and the simple phratry and female descent, up to tribes which have lost their classes and totems, count descent in the male line, and permit marriage only between persons dwelling in certain localities, or not of 'too near flesh.' All sorts of varieties of custom, in fact, prevail. Again, the most backward tribes, in Mr. Howitt's opinion, have group-marriage;67 the more advanced have individual marriage, with rare reversions on special occasions. Each advance, from mere phratry to phratry plus eight 'classes,' reduced the number of persons who might intermarry, and extended the range of exogamy (except where, as among the Arunta, the totem prohibition has ceased to exist). The marked tendency of the developing rules is to prevent marriage between persons 'too near in flesh,' or 'of the same flesh.' Mr. Howitt argues that, if the later stages of prohibition are the result of deliberate intention to prevent too near marriage, we may infer that the original 'bisection' of the 'undivided commune' was also consciously designed to prevent unions of persons of too near flesh.
To this I would reply, that the circumstances were different. The savages of recent centuries have been trained in the totem and phratry systems, and have now, like Mr. Howitt, excogitated the theory that these were originally designed for the purpose of preventing marriages of 'too near flesh,' wherefore all such marriages (even if permitted by the totem law) must be morally or materially evil. This is the theory expressed in the myths of the Dieri, Woeworung, and others; and it is the theory of many scientific writers. In brief, it is the hypothesis of men already trained to think near marriages morally wrong, or physically injurious. But how could this idea occur to members of 'an undivided commune,' who had never known anything better?
That is the difficulty; and we get rid of it by disbelieving in a primeval undivided commune; and by supposing a long past of forbidden unions, the prohibition then resting on no moral ideas, but on the interest of the strongest, the jealousy of the adult sire. These prohibitions later evolved into conscious morality; and were at last susceptible of improvement by deliberate design. I shall now examine more in detail the ideas which do not win my assent.
MR. FISON ON THE GREAT BISECTION
In 1880, in Kamilaroi and Kurnai,68 Mr. Fison, a learned missionary and anthropologist, gave his account of the organisation of certain Australian tribes. He speaks of (1) The division of a tribe, or community, into two exogamous intermarrying classes.69 (2) 'The subdivision' (mark the phrase) 'of these classes into four.' (3) 'Their subdivision into gentes, distinguished by totems, which are generally, though not invariably, the names of animals.'
Now totems we know, and we have cited Mr. Mathews for the other divisions. Take (1) 'the two exogamous intermarrying classes.' Examples are
Male, Kumite; female, Kumitegor (one 'class,' which I call 'phratry').
Male, Kroki; female, Krokigor (the other 'class,' 'phratry').
Again.
Male, Yungaru (opossum); female, Yungaruan.
Male, Wutaru (kangaroo); female, Wutaruan.
What are these two 'primary' exogamous divisions? And why call them 'primary'?
'PRIMARY CLASSES?'
My object, as has been said, is now, contrary to general opinion, to repeat that the great dichotomous 'division' of a tribe into two exogamous, intermarrying, 'classes' or 'phratries,' is not 'primary' at all, but is secondary to groups at once totemic and exogamous, and is not, in origin, a bisection, but a combination. If I am right, the consequences will be of some curiosity. First, it will appear that the 'primary divisions' are themselves totemic in origin, thus implying the pre-existence of Totemism. Next it will be made to appear probable that the pre-existing totems were already exogamous before the phratries arose, and that exogamy does not date, as the best authorities hold, from the making of the great dichotomous divisions or 'phratries.' For no such dichotomous division, I suggest, was ever made.
THE 'PRIMARY DIVISIONS' ARE THEMSELVES TOTEMIC AND EXOGAMOUS
We see that, of the two 'phratries' Yungaru and Wutaru, Yungaru is 'opossum' (according to Mr. Chatfield) or 'alligator' (according to Mr. Bridgman); while Wutaru is 'kangaroo.' These two primary 'phratries,' therefore, have totemic names, and (in my opinion) were originally two local totem groups, each containing members of various totems derived from alien mothers. The same thing may be true when the meanings of the 'primary class names' ('phratries') can no longer be discovered. If so, the 'primary divisions' are, in origin, mere totem distinctions, involving, I think, the pre-existence of the rule of exogamy, which is also involved in the rules of the 'primary divisions.' Mr. Fison writes (what is obvious) 'in some places the primary divisions are distinguished by totem names at the present day.'70
'Probably they were so distinguished everywhere, in ancient times,' he adds, and this is certainly the case in North America, as we shall see later. Mr. Fison's opinion is my own so far, and, if it is right, if the 'primary class divisions' ('phratries'), within which marriage is now forbidden, were originally two totem divisions, then Totemism is earlier than the 'primary divisions.' On this point Messrs. Fison and Howitt say that the divisions on which marriage regulations are based 'are denoted by class names or by totems – frequently by both class names and totems.' In a note they add, 'Class names, so called by us solely for the sake of convenience, and because they cannot always be positively asserted to be totems, though the strong probability is that they are always totems.'71
By 'class names' the authors, I think, here mean the names of the 'primary exogamous divisions' or 'phratries.' These are often, if not always, known by totem names. But the 'classes,' as distinguished from the 'phratries,' are not known by totemic names, as far as I am aware. Herr Cunow, we shall see, asserts that in some cases they denote mere seniority, 'big' and 'little,' 'young' and 'old.' Unless they can be proved to be totemic, we must, I repeat, carefully avoid confusing the 'classes,' four or eight, with the 'phratries,' in which they are included. The confusion is general and very misleading.
Totemism, according to Mr. McLennan, preceded exogamy, and made exogamy possible. Thus totem distinctions, with exogamy, may be older than the 'two primary class exogamous divisions,' in which, according to most authorities, exogamy began. Mr. Tylor is cautious: 'the dual form of exogamy' (the 'phratries,' or 'two primary divisions') 'may be the original form,' or at least that view is tenable.72 The origin of exogamy is, however, unknown, in Mr. Tylor's opinion, which commits him to nothing.
Mr. Howitt, if I do not misinterpret him, also regards the two divisions, 'phratries,' as primary, but at the same time agrees with me, and Mr. Fison, that the two 'phratry' divisions were themselves in origin totemic.
THE TOTEM DIFFICULTY
At this point I lose Messrs. Fison and Howitt. I do not know what they mean, and, unless I misconstrue them, they unconsciously hold different opinions at different moments. They start with an 'undivided commune.' Mr. Fison, however, is not certain on this point. To prevent near marriages (previously universal), the commune is split into two exogamous intermarrying phratries. The names of these phratries are totemic, and each phratry has its totem. Such is their theory. How and why?
Did totemic divisions already exist in 'the undivided commune'? If so, the commune was not undivided! Or were totem names given, nobody knows why, to the two phratries at the time when the 'bisection' of the commune was made? Did the legislator send half the horde to the right, crying, 'You are sheep,' and half to the left, saying, 'You are goats,' – or rather, say, Emus and Kangaroos? This is not easily thinkable. But, if this was done, whence came the other totem kins, often numerous, within each phratry?
Mr. Fison says that the totem kins (or 'gentes') 'arose out of two primary divisions, by an orderly process of evolution, such as might be expected from the forces at work,' and 'we have seen how' the phratries subdivided 'into other subdivisions, distinguished by totems.'73 But, alas, I have seen nothing of the sort! Mr. Fison has merely asserted the fact. 'The totems affect the intersexual regulations … by narrowing the range of matrimonial selection.'74 Here would be a reason for the evolution of these totem kins. But this added restriction is exactly what (given phratries) the totems do not effect. There are so many totems in each phratry, but as the same totem (except among the Arunta and similarly disorganised tribes) never occurs in both phratries, the range of sexual selection is thus not more restricted by the totem than by the phratry. The members of each phratry may not intermarry, and all persons of their totem are in their phratry and so are not marriageable to them. They would all be exactly as exogamous as they are, if there were no totem rules, nothing but phratry rules. Thus the totems cannot be later deliberate segmentations of the phratry, for additional exogamous purposes, because they serve no such purpose, except where, among the Kamilaroi, a man may marry in his phratry, if he marries out of his totem. But that is a peculiarity.
Mr. Mathews writes, 'Under the group' (phratry) 'laws it is impossible for a Dilbi or Kupathin' (phratry names of the Kamilaroi) 'to marry a woman bearing the same totem name as himself, for the reason that such a totem does not exist in the division' (phratry) 'from which he is bound to select his wife. But when persons of the same group' (phratry) 'were permitted to marry each other, it became necessary to promulgate a law prohibiting marriage between persons of the same totem.'75 But there were totems before that novelty of marriage within the phratry, and why were they there? Moreover, under phratry laws it was already the rule that no man could marry a woman of his own totem. Obviously we are not told how the totem kins arose out of the phratries, 'by an orderly process of evolution such as might be expected from the forces at work.' One sees no reason at all for the rise of totem kins within the phratry, itself, by Mr. Fison's theory, originally totemic.
Totem kins are called 'subdivisions' by Mr. Howitt, but why were the phratries subdivided into totem kins, and why were there totem groups in 'the undivided commune' before the bisection, the phratries (the result of the bisection) being themselves, in Mr. Howitt's hypothesis, totem groups? I quote a statement of the case by Mr. Howitt (1889): 'The fundamental principle of aboriginal society in Australia is the division of the community into two exogamous intermarrying moieties. Out of this division into two groups, and out of the relations thus created between the contemporary members of them and their descendants, the terms of relationship must have grown. As the two primary divisions (classes)' ('phratries') 'have become again divided in the process of social development, and as the groups of numerous totems have been added,' &c.76
Here the totem kins are not orderly evolved out of the phratries, nor subdivided out of them, but are 'added.' Where were they picked up, whence did they arise, why were they 'added'?
May we not conclude that no clear account, or theory, of the origin and purpose of totems and totem kins has been laid before us?
Mr. Howitt elsewhere writes, 'If the supposition is correct that, in the primary divisions, we may recognise the oldest forms, and in the subdivisions somewhat newer forms of Totemism' (newer names of totems?), 'it should be found that these earlier divisions show signs of antiquity as compared to the totems which are, according to this hypothesis, the nearest to the present time. This, I think, is the case.' Thus, in fact, some of the Australian names for the two divisions are no longer to be translated,77 perhaps owing to their antiquity, and sometimes the names are lost, as, elsewhere, in Banks Island. When translatable, the phratry names are totemic.
But this hardly amounts to proof that the 'primary divisions' are really older than totemic divisions, plus exogamy. The existing names of the 'primary divisions' may be older than existing totem names, in some cases. But that may be because the two 'primary divisions' endure, unchanged, while a local totem group may become extinct.78 Its place, perhaps, may be filled up by a totem group of relatively recent name, or, perhaps, in a great trek into a land of novel fauna and flora, old totem names might be exchanged for new ones. 'Munki' (sheep) is said to have been recently adopted.79 Mr. Fison here corroborates my suggestion. 'If a tribe migrate to a country in which their totem is not found, they will, in all probability, take as their totem some other animal which is a native of the place.'80
Mr. Howitt, then, believes that 'the primary class divisions' were originally totemic, and also that the 'class system' as a rule has been developed through the subdivision of the earlier and simpler forms by 'deliberate arrangement.'81
This appears to mean that savages began by making two divisions, bearing totem names, and established them as primary exogamous divisions. Later they cut them up into slices, each slice with a newer totem name. Or the totem divisions are evolved within the phratry, somehow or other, as in one of Mr. Fison's views. Or they are 'added' – for what purpose? Thus every tribesman has now a 'class name' (phratry name) – an old totem name (say either Eagle-Hawk or Crow), and no Crow may marry an Eagle-Hawk. But, later, they split Crows up into, say, bats, rats, cats, and kangaroos, while they split Eagle-Hawk up into, say, grubs, emus, mice, and frogs. Now each person, under this arrangement, has two totem names. He is Eagle-Hawk (old) and (new) grub, emu, mouse, or frog: or he is Crow (old) and (new) bat, cat, rat, or kangaroo. If cat, he may not only not marry a Crow, but also he may not marry a cat. What could be the reason for this new subdivision of Eagle-Hawk and Crow, and for this multiplication of marriage prohibitions, which, given the phratries, prohibit nothing?82 I shall try to show, and have already suggested, that, from a period infinitely remote, each member of the Eagle-Hawk and Crow local groups may also have been, or rather must have been, a grub, emu, mouse, or frog, bat, rat, cat, or kangaroo, by inheritance and birth. So understood, the 'primary divisions' (Eagle-Hawk and Crow) were not deliberately subdivided (as I conceive them to have been on Mr. Ho wit Vs system) into the other numerous new totem groups, nor were the totem kins added to the phratries, nor were they orderly evolved out of the phratries, but, from the dawn of Totemism with exogamy, they contained these totem groups within themselves; a fact which early man came to perceive.
Mr. Howitt adds, 'If the two first intermarrying groups' ('phratries') 'had distinguished names, they were probably those of animals, and their totems, and, if so, the origin of Totemism would be so far back in the mist of ages, as to be beyond my vision.' In the chapter on the 'Origin of Totemism,' we try to penetrate 'the mist of ages,' and to see beyond the range of vision of Mr. Howitt. But the 'Origin of Totemism' cannot be beyond Mr. Howitt's range of vision, if he agrees with Mr. Fison that the totem kins were orderly evolved within the phratry, or were segmented out of the phratry, or split off, as colonies, from the phratry (Dr. Durkheim's theory), or were added to the phratry, for some reason.
It seems, then, that he does not commit himself to any of these four theories. He appears to confess to having no theory of the origin of Totemism, which, in his opinion, gave the names to the phratries, these being the result of the primary bisection. Probably his best plan would be to say 'the horde was bisected into two moieties, for exogamous purposes, and animal names, for the sake of distinction, were arbitrarily imposed on the phratry divisions.' But, then, what about the many totem kins within the phratry? We receive no solid theory about them. They were certainly not arbitrarily marked out later, within the phratry, for exogamous purposes which they do not fulfil. If they were picked up elsewhere, and added into the phratry, where did they come from? Crowds of totems were not going about, Mr. Howitt seems to think, before the bisection, because, if so, we saw hordes were not 'undivided,' before the bisection, but were already divided into totem kins.
Or shall we say that the undivided communes had already organised distinct co-operative magical totem groups, to do magic for the good of the food supply, plants and animals, but that these totem groups were not exogamous before the bisection? After the bisection two of these magical totem groups, say Eagle-Hawk and Crow, were selected, shall we guess, to give names to the two moieties or phratries? The other totem groups fell, or were meted out, some into Crow, some into Eagle-Hawk. This is a thinkable hypothesis, but it is fatal to the theory of subdivision, or of segmentation, or of evolution, as causes of totem kins within the phratries; and it is not suggested by Messrs. Fison and Howitt.
Thus we must construct for ourselves, later, a theory of the Origin of Totemism. We are actually constrained to make this effort, because it will probably be admitted that, having no theory, or hesitating between three or four theories, of the origin of totems and of totem kins, Messrs. Fison and Howitt produce an hypothesis of the evolution of Australian society which cannot be construed by us into an intelligible form.






